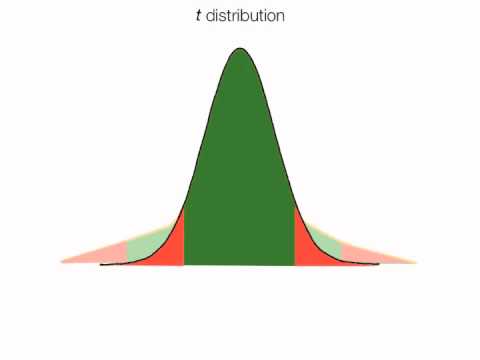
In this tutorial, I'm going to talk about the T distribution. The T distribution is very similar to the z-score. I'm going to review a little bit of that as well. But first, I want to tell you a little bit about the history of the T distribution. Normally, I don't talk about these things, but this is William Gossett, and what makes him interesting is that he actually used the T distribution to help improve Guinness beer where he worked. So, he helped make tasty beer. Now, the normal distribution looks like this. In the green area, we have the acceptance area, and in the red area, we have the rejection regions. This is called a two-tailed test. 95% of the area of the curve is in the green area, and 5% are in the rejection area, or 2.5% in each tail. Sometimes, the tails are referred to as alpha. If you're in a fraternity or sorority, you probably know that already. And that's equal to 0.05. Sometimes, it's called a p-value, which is also known as the probability value or the p-value. Now, we have the z-scores. The z-scores are 1.96 and -1.96. Remember, that's the number of standard deviations away from the mean. 1.96 is just about 2, and that's important because I tell my students, you know when you get to 2, it's a lot easier to remember than 1.96. This 2 value is going to be important for T statistics as well or the T distribution. Also, we write it like this: if Z is less than or equal to -1.96 or if Z is greater than 1.96, we reject the null hypothesis. Or if Z is about 2 or -2. Now, the T distribution or T test looks about like this, with a little...
Award-winning PDF software





Video instructions and help with filling out and completing How Form 2220 Calculator